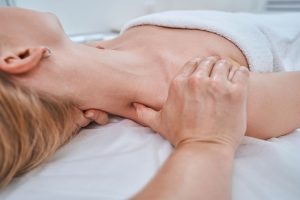
Manual therapy is a hands-on approach to treating musculoskeletal pain and dysfunction. It’s used by physical therapists, chiropractors, and other healthcare professionals to help patients achieve pain relief, improved mobility, and overall physical rehabilitation. This article will delve into what manual therapy is, explore various techniques used, and highlight the benefits for those seeking pain relief and physical rehabilitation.
What is Manual Therapy Defining Manual Therapy
Manual therapy involves the use of the practitioner’s hands to manipulate the muscles, joints, and soft tissues of the body. This hands-on approach aims to decrease pain, increase range of motion, reduce inflammation, and improve function.
History of Manual Therapy
Manual therapy has been practiced for centuries, with roots in ancient Chinese and Greek medicine. Over time, it has evolved into a scientifically-based treatment method, incorporating evidence-based techniques to address a wide range of physical issues.
Techniques Used in Manual Therapy
Joint Mobilization
Joint mobilization is a technique that involves passive movement of specific joints to restore normal movement patterns. This technique is often used to treat joint stiffness and pain.
Grades of Mobilization
- Grade I: Small, gentle oscillations at the beginning of the range of motion.
- Grade II: Larger movements within the range of motion but not reaching the limit.
- Grade III: Large movements up to the limit of the range of motion.
- Grade IV: Small, oscillatory movements at the limit of the range of motion.
- Grade V: A quick, small movement beyond the limit of the range of motion (also known as manipulation).
Soft Tissue Techniques
Soft tissue techniques focus on the muscles, fascia, and other connective tissues. These techniques aim to reduce tension, increase blood flow, and promote healing.
Types of Soft Tissue Techniques
- Myofascial Release: Involves applying sustained pressure to the myofascial connective tissue to eliminate pain and restore motion.
- Trigger Point Therapy: Targets specific areas of muscle tightness (trigger points) that can cause pain in other parts of the body.
- Massage: Uses various strokes and pressures to relax muscles, improve circulation, and reduce pain.
Muscle Energy Techniques (MET)
Muscle Energy Techniques are a form of manual therapy that uses the patient’s muscle contractions to mobilize joints and relax muscles. This technique involves the patient actively contracting a muscle against a counterforce applied by the therapist.
How MET Works
The therapist positions the patient so that the muscle to be treated is stretched to the point of resistance. The patient then contracts the muscle against the therapist’s resistance for a few seconds, followed by relaxation and a further stretch.
Benefits of Manual Therapy
Pain Relief
One of the primary benefits of manual therapy is pain relief. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue work can reduce pain by improving joint function, decreasing muscle tension, and promoting the release of endorphins.
Improved Mobility
Manual therapy can help restore normal movement patterns by reducing joint stiffness and muscle tightness. This is particularly beneficial for patients with conditions such as arthritis, frozen shoulder, and post-surgical stiffness.
Enhanced Healing
By improving blood flow and reducing inflammation, manual therapy can enhance the body’s natural healing processes. This can lead to faster recovery times for injuries and surgeries.
Physical Rehabilitation
Manual therapy plays a crucial role in physical rehabilitation. It helps to restore function and movement, enabling patients to return to their daily activities and sports more quickly.
Personalized Treatment
One of the strengths of manual therapy is its personalized approach. Therapists tailor their techniques to meet the specific needs of each patient, ensuring optimal results.
Non-Invasive Treatment
Manual therapy offers a non-invasive alternative to medications and surgery. It provides a natural way to manage pain and improve function without the risks associated with more invasive treatments.
Common Conditions Treated with Manual Therapy
Back and Neck Pain
Manual therapy is highly effective in treating back and neck pain. Techniques such as joint mobilization and soft tissue work can alleviate pain and improve mobility in these areas.
Sports Injuries
Athletes often benefit from manual therapy to recover from injuries such as sprains, strains, and overuse injuries. The hands-on approach helps to reduce pain, improve flexibility, and restore function.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
After surgery, manual therapy can help patients regain mobility, reduce pain, and speed up the recovery process. Techniques are adapted to ensure safety and effectiveness during the healing phase.
Chronic Pain Conditions
Conditions like fibromyalgia and chronic fatigue syndrome can be managed with manual therapy. The gentle techniques used can help reduce pain and improve overall well-being.
Headaches and Migraines
Manual therapy can be beneficial for patients suffering from tension headaches and migraines. Techniques that address muscle tension and joint dysfunction in the neck and upper back can help reduce the frequency and severity of headaches.
Finding a Qualified Manual Therapist
What to Look For
When seeking a manual therapist, it’s important to find someone who is highly trained and experienced. Look for therapists who are licensed and have certifications in manual therapy techniques. There are various levels of training and credentialing available. Some therapists will take a few weekend courses, others are certified in a specific manual therapy approach and others will reach the highest level of training which is a fellowship in manual therapy that is nationally credentialled by the American Academy of Orthopedic Manual Physical Therapists. You can locate a manual therapy fellow through their website: Find-A-Fellow | AAOMPT
Questions to Ask
- What is your training and experience in manual therapy?
- What techniques do you specialize in?
- Can you provide references or testimonials from past patients? Do you have any specific credentialing or certifications in manual therapy?
Importance of Communication
Effective communication between you and your therapist is crucial. Be sure to discuss your symptoms, medical history, and treatment goals to ensure that the therapy is tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Manual therapy is a powerful tool for pain relief and physical rehabilitation. With its hands-on approach and personalized treatment plans, it offers a natural and effective way to manage a variety of conditions. Whether you’re dealing with chronic pain, recovering from an injury, or looking to improve your mobility, manual therapy can provide significant benefits. If you’re interested in exploring manual therapy, contact Manual Therapy Associates for expert care and tailored treatment.
Check out our Facebook for more inquiries!
FAQs
Is manual therapy painful?
Manual therapy is generally not painful. Some techniques might cause temporary discomfort, but therapists aim to make the treatment as comfortable as possible.
How long does a manual therapy session last?
Sessions typically last between 30 to 60 minutes, depending on the treatment plan and the specific needs of the patient.
How many sessions will I need?
The number of sessions required varies based on the individual’s condition and response to treatment. Your therapist will provide a tailored treatment plan with an estimated number of sessions.
Can manual therapy be combined with other treatments?
Yes, manual therapy is often combined with other treatments such as exercise, medication, and other physical therapy techniques for a comprehensive approach.
Is manual therapy covered by insurance?
Most insurance plans will cover manual therapy when it is part of a physical therapy program. Unfortunately, many manual therapy specialists are no longer in-network with most commercial insurance plans. A specialized manual therapy practice often does not fit the standard insurance model of care which requires a higher volume of patients and utilization of support staff to carry out a plan of care. Although this may be the case, many people still find that the quality and specificity of care provided by a manual therapy fellow ultimately saves money as the recovery has been shown to be faster and completed in fewer visits.